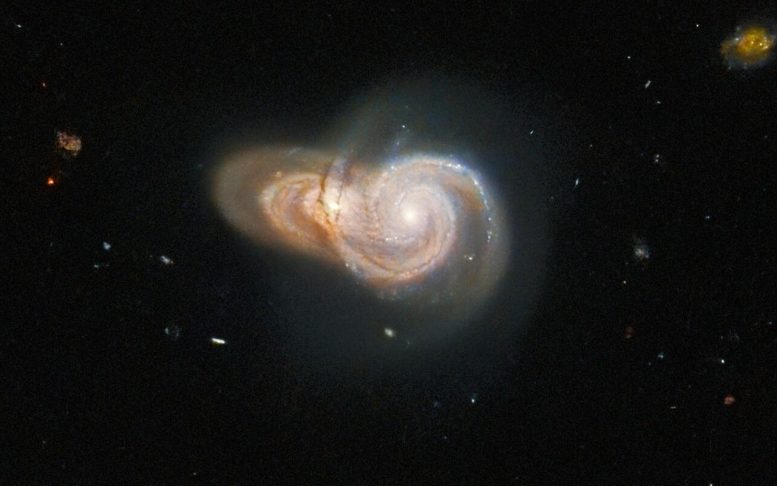
Imagen del telescopio espacial Hubble de dos galaxias espirales superpuestas, SDSS J115331 y LEDA 2073461. Crédito: ESA/Hubble y NASA, W. Keel
Dos galaxias espirales superpuestas se representan en esta maravillosa imagen de[{» attribute=»»>Hubble Space Telescope. The two galaxies, which lie more than a billion light-years from Earth, have the uninspiring names SDSS J115331 and LEDA 2073461. Although they appear to collide in this image, the alignment of the two galaxies is likely just by chance — the two are not actually interacting. Although these two galaxies might simply be ships that pass in the night, Hubble has captured a dazzling array of interacting galaxies in the past.
This image is one of many NASA/ESA Hubble observations delving into highlights of the Galaxy Zoo project. Originally established in 2007, the Galaxy Zoo project and its successors are massive citizen science projects which crowdsource galaxy classifications from a pool of hundreds of thousands of volunteers. These volunteers classify galaxies imaged by robotic telescopes and are often the first to ever set eyes on an astronomical object.
Over the course of the original Galaxy Zoo project, volunteers discovered a menagerie of weird and wonderful galaxies including unusual 3-armed spiral galaxies and colliding ring galaxies. The astronomers coordinating the project applied for Hubble time to observe the most unusual inhabitants of the Galaxy Zoo — but true to the project’s crowdsourced roots, the list of targets was determined by a public vote.

«Alborotador. Amante de la cerveza. Total aficionado al alcohol. Sutilmente encantador adicto a los zombis. Ninja de twitter de toda la vida».






More Stories
Una imagen inquietante de la superficie de Marte
¿Júpiter tiene anillos? Sí, lo es
El efecto de la dieta sobre las bacterias intestinales proporciona nuevas pistas en el tratamiento de la enfermedad de Parkinson